CCRN Pneumothorax
CCRN Pneumothorax Overview
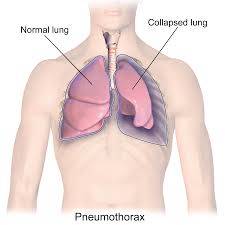
Pneumothorax
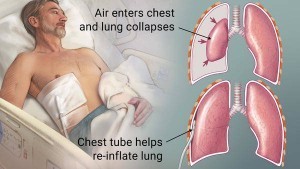
A pneumothorax is an abnormal collection of air or gas in the pleural space that causes an uncoupling of the lung from the chest wall. Like pleural effusion (liquid buildup in that space), pneumothorax may interfere with normal breathing. It is often called collapsed lung, although that term may also refer to atelectasis. One or both lungs may be affected. A primary pneumothorax is one that occurs spontaneously without an apparent cause and in the absence of significant lung disease, while a secondary pneumothorax occurs in the presence of existing lung pathology. Pneumothoraces can be caused by physical trauma to the chest (including blast injury), or as a complication of medical or surgical intervention; in this case it is referred to as a traumatic pneumothorax. In a minority of cases of both spontaneous or traumatic pneumothorax, the amount of air in the chest increases markedly when a one-way valve is formed by an area of damaged tissue, leading to a tension pneumothorax. This condition is a medical emergency that can cause steadily worsening oxygen shortage and low blood pressure. Unless reversed by effective treatment, these sequelae can progress and cause death.Signs and Symptoms
-
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Decreased or absent breast sounds on the affected side
- Agitation
- Tachycardia
Causes
A pneumothorax can be caused by:- Chest injury. Any blunt or penetrating injury to your chest can cause lung collapse. Some injuries may happen during physical assaults or car crashes, while others may inadvertently occur during medical procedures that involve the insertion of a needle into the chest.
- Lung disease. Damaged lung tissue is more likely to collapse. Lung damage can be caused by many types of underlying diseases, including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), cystic fibrosis and pneumonia.
- Ruptured air blisters. Small air blisters (blebs) can develop on the top of your lung. These blebs sometimes burst — allowing air to leak into the space that surrounds the lungs.
- Mechanical ventilation. A severe type of pneumothorax can occur in people who need mechanical assistance to breathe. The ventilator can create an imbalance of air pressure within the chest. The lung may collapse completely.
Risk Factors
Risk factors for a pneumothorax include:- Sex. In general, men are far more likely to have a pneumothorax than are women.
- Smoking. The risk increases with the length of time and the number of cigarettes smoked, even without emphysema.
- Age. The type of pneumothorax caused by ruptured air blisters is most likely to occur in people between 20 and 40 years old, especially if the person is a very tall and underweight.
- Genetics. Certain types of pneumothorax appear to run in families.
- Lung disease. Having an underlying lung disease — especially chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) — makes a collapsed lung more likely.
- Mechanical ventilation. People who need mechanical ventilation to assist their breathing are at higher risk of pneumothorax.
- Previous pneumothorax. Anyone who has had one pneumothorax is at increased risk of another, usually within one to two years of the first.
Diagnosis
- A pneumothorax is diagnosed by a combination of signs and symptoms, chest X-ray, and CT scan of the chest
Treatment
- Chest tube insertion on the affected side
- Possible needle decompression
- Oxygen
- Pain medications
- Monitor VS
- ICU admission if severely compromised
Critical Care Courses
Overview
- Elite Reviews Offers A Variety Of Online Courses That Will More Than Adequately Help Prepare The Critical Care Nurse To Pass The National Exam.
- Each Course Includes Continuing Education Credit and Sample Questions.
Continuing Education
- Each Of Our Online Courses Has Been Approved Continuing Education Contact Hours by the California Board of Nursing
- Login To Your Account In Order To Access The Course Completion Certificate Once The Course Is Complete.
CCRN Free Trial
- FREE Sample Lecture & Prep Questions
- Available For 24 Hrs After Registration
- Click Free Trial Link To Get Started - CCRN Free Trial
How It Works
How It Works
- First - Purchase The Course By Clicking On The Blue Add To Cart Button - You Will Then Be Prompted To Create A User Account.
- Second - After Creating An Account, All 3 Options (90, 120 or 150 Days) Will Be Listed. Select The Option You Desire And Delete The Other Two.
- Third - You Will Be Prompted To Pay For The Review Using PayPal - After Payment You Will Be Redirected Back To Your Account.
- Last - Click The Start Button Located Within Your Account To Begin The Program
- 150 Sample Questions
- Q & A With Rationales
- Approved For 5 CEU's
- 90 Days Availability
- Cost $75.00
- 1250+ Sample Questions
- Q & A With Rationales
- Approved For 25 CEU's
- 90 Days Availability
- Cost $200.00
CCRN Practice Questions Bundle
- 1350+ Sample Questions
- Q & A With Rationales
- Approved For 30 CEU's
- 90 Days Availability
- Cost $225.00
CCRN Review Course
- Option 1
- Lectures & 1250+ Questions
- Approved For 35 CEU's
- 90 Days Availability
- Cost $325.00
- Option 2
- Lectures & 2000+ Questions
- Approved For 40 CEU's
- 90 Days Availability
- Cost $350.00
CCRN Review Course Bundle
- Option 3
- Lectures & 3000+ Questions
- Approved For 70 CEU's
- 90 Days Availability
- Cost $375.00